Publication date: Decembre 13, 2024
Are you interested in investing or want to learn more about the financial markets? Then you have probably come across the term AEX. But what does the AEX entail? In this article, we explain what the AEX index is, how it is structured, and which stocks are traded on this iconic Dutch exchange. Additionally, we discuss why the AEX is so important for investors and how movements in this index are often seen as a reflection of the Dutch economy. Whether you are a beginner investor or just curious about financial trends, here you will find all the essential information about the AEX

What is the AEX?
The AEX, or Amsterdam Exchange Index, is the most well-known stock index in the Netherlands and an important benchmark for the Dutch economy. This index consists of the 25 largest and most traded companies listed on the Amsterdam stock exchange, part of Euronext. Think of major names like ASML, Shell, and ING, which are often active worldwide and enjoy international recognition.
Click HERE for the composition of the AEX as of June 28, 2024.
For someone starting to explore the stock market, the AEX provides a clear introduction to the largest and most influential companies in the Netherlands. The index functions as a kind of barometer: rising stock prices within the index lead to an increase in the AEX, while falling prices have the opposite effect. This makes the AEX a practical indicator of the overall sentiment on the Dutch stock exchange.
For more experienced investors, the AEX is not only a source of market insights but also a reference point for comparing the performance of their portfolios. The companies in the index play a significant role in sectors such as technology, energy, and finance, making the AEX internationally relevant as well. Whether you are a novice investor or have been active in the markets for years, the AEX provides valuable information and remains an indispensable benchmark for the financial world.
The Origins of the AEX
The AEX, or Amsterdam Exchange Index, was established in 1983 by the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, one of the oldest stock exchanges in the world. The index emerged from the need for a clear benchmark for the performance of the most important publicly listed companies in the Netherlands. Initially, the index was known as the EOE index, named after the European Options Exchange. At its inception, the index included 13 companies, which later grew to the current 25.
Investing in the AEX
Investing in the AEX offers various advantages for both beginner and experienced investors. The index consists of 25 of the largest and most stable companies in the Netherlands, often with a strong international presence. This means that by investing in the AEX, you gain direct exposure to some of the key sectors, such as technology, energy, and finance, which have a significant impact on the global economy.
Another benefit of investing in the AEX is the diversification that the index provides. By investing in the index, for example through an ETF (Exchange Traded Fund), you automatically spread your investment across multiple companies. This reduces the risk associated with investing in a single stock. Additionally, the AEX is seen as a reliable benchmark for the Dutch economy, making it an attractive choice for investors who specifically have confidence in the economic outlook for the Netherlands.
Moreover, the AEX is relatively transparent and easy to follow. The performance of the companies in the index is published daily, making it simple to keep track of trends and developments. For many investors, it is therefore an appealing option for both long-term growth and capitalizing on market developments.
The evolution of the AEX: From then to now
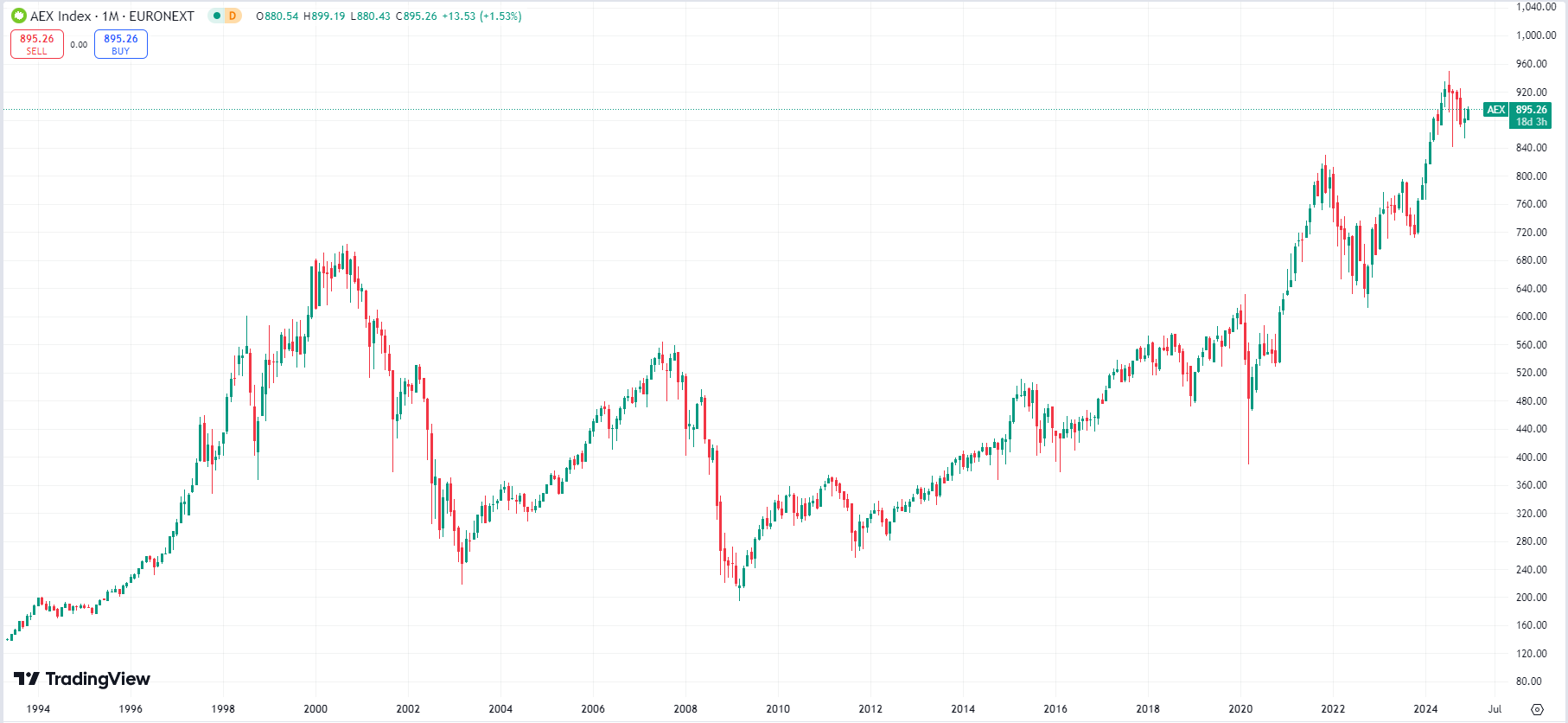
Since 1990, the AEX began to undergo significant price developments that were closely linked to the economic conditions and market dynamics of the time. In the early 1990s, the index started with a value of around 300 points. Throughout the decade, the AEX steadily rose, with a notable increase during the period of the dot-com bubble at the end of the 1990s. In 2000, the AEX reached a record high of over 650 points, driven by the strong growth of technology companies and optimism about the digital future.
However, after the peak in 2000, a sharp correction followed, caused by the dot-com crisis. The AEX experienced a significant decline in the subsequent years, reaching a low of approximately 240 points in 2003. This period of volatility highlighted the vulnerability of the stock markets. Nevertheless, the AEX gradually recovered in the following years, with stabilization and growth in price development.
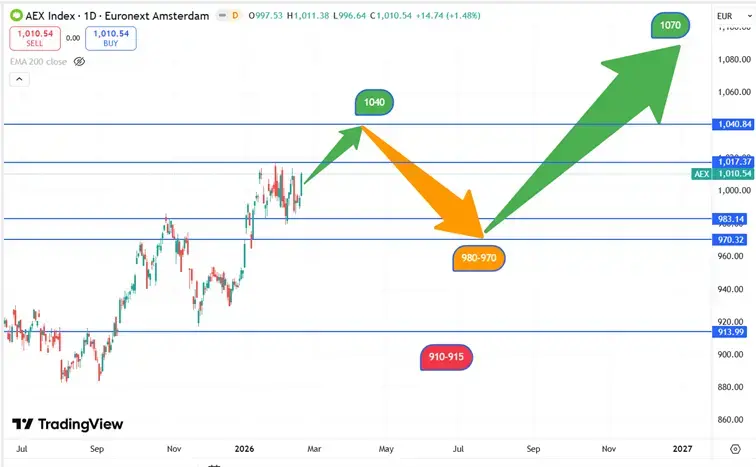
In the years that followed, the AEX made a remarkable recovery and strengthened its position as an important indicator of the Dutch economy. Since then, the index has experienced consistent growth, thanks in part to the strong performance of companies in sectors such as technology, renewable energy, and financial services. You can see this illustrated in the graph below.
Periodic changes in the weights of the AEX Index
The AEX index, as the primary benchmark for the Dutch stock market, undergoes periodic changes in the weights of the companies included in it. These changes typically occur quarterly and are based on the market capitalization of the companies. Market capitalization is the total value of a company, calculated by multiplying the share price by the number of outstanding shares. As a result, larger companies have a greater impact on the index than smaller ones. However, trading volume can also affect the index, especially regarding liquidity and the ability of investors to enter and exit positions. High volumes can indicate strong interest and may also influence the price movements of stocks. If there is significant demand for shares with high market capitalization, this can further impact the index value.
The reason for these periodic revisions is to ensure that the AEX remains an accurate and up-to-date reflection of the performance of the most influential publicly listed companies in the Netherlands. When a company experiences a significant increase or decrease in its market capitalization or trading volume, this can affect the weighting of that company within the index. For example, if a large company like ASML increases in value, it may represent a larger percentage of the index, which can push the overall index value higher. Conversely, a decline in a company's value can lead to a lower weighting and a negative impact on the index.
These periodic changes are crucial for investors, as they not only influence the composition of the index but also the overall performance of the AEX. Investors need to be aware of these changes, as they can lead to fluctuations in the index that affect investment strategies. Furthermore, investors who invest in the AEX through Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) or index funds can benefit from these changes by achieving broader diversification and exposure to the strongest companies in the Netherlands.

.svg)


.webp)

.webp)
.webp)